Respiratory Disorders
Respiratory Disorders
There are a number of respiratory disorders which affect people. The percentage of
such disorders is particularly high in Pakistan. It is due to the more concentration of
air pollutants not only in the urban but also in the rural atmosphere.
Some of the
important respiratory disorders are described next
1. Bronchitis:
Bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchi or bronchioles. It results in excessive
secretions of mucus into the tubes, leading to the swelling of tubular walls and narrowing
of tubes. It is caused by viruses, bacteria or exposure to chemical irritants
(e.g. tobacco smoke).
There are two major types of bronchitis i.e. acute and chronic.
The Acute Bronchitis
usually lasts about two weeks and patients recover with no permanent damage to
the bronchi or bronchioles.
In Chronic Bronchitis, the bronchi develop chronic
inflammation. It usually lasts for three months to two years.
Symptoms of bronchitis include a cough, mild wheezing, fever, chills and shortness of
breath (especially when doing hard job).

2. Emphysema:
Emphysema is the destruction of the walls of the alveoli. It results in larger sacs but
with less surface area for gaseous exchange . As lung tissue breaks down,
the lungs do not come back to their original shape after exhalation. So air cannot be
pushed out and is trapped in the lungs.
The majority of people diagnosed with chronic bronchitis are 45 years of age or older.
The Symptoms of emphysema
include shortness of breadth,
fatigue, recurrent respiratory
infections and weight loss.
By the time the symptoms of emphysema
appear, the patient has usually lost
50% to 70% of his / her lung tissue.
The level of oxygen in blood may
get so low that it causes serious
complications.
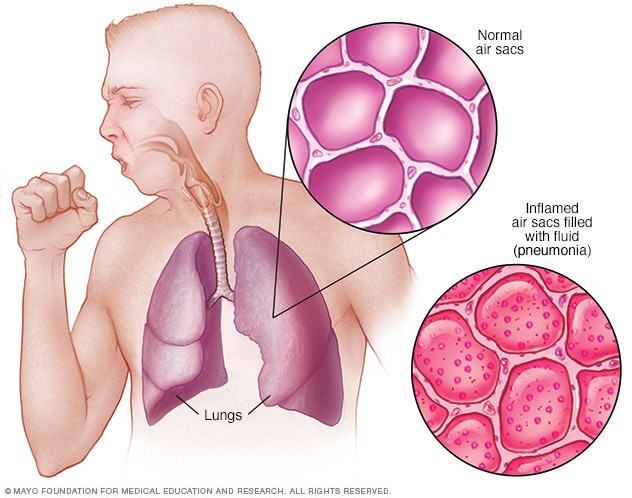
3. Pneumonia:
Pneumonia is an infection of
lungs. If this infection affects both
lungs then, it is called double pneumonia. The most common Cause of pneumonia is a
bacterium, Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Some viral (influenza virus) and fungal infections may also lead to pneumonia. When
the causative organisms enter the alveoli, they settle there and grow in number. They
break the lung tissues and the area becomes filled with fluid and pus. The symptoms
of pneumonia include a cold that is followed by a high fever, shivering, and a cough
with sputum production. Patient may become short of breath. The patient’s skin colour
may change and become dusky or purplish. It is due to poor oxygenation of blood.
Vaccines are available to prevent pneumonia caused by S. pneumoniae. Antibiotics are
used in the treatment of this type of pneumonia.
Prior to the discovery of antibiotics, one-third of pneumonia patients died from the infection.
4. Asthma:
Asthma is a form of allergy, in which
there is inflammation of the bronchi,
more mucous production and
narrowing of the airways .
In asthma patients, the bronchi and
bronchioles become sensitive to
different allergens (allergy causing
factors) e.g. dust, smoke, perfumes,
pollens etc. When exposed to any of
such allergens, the sensitive airways
show immediate and excessive
response of constriction. In this
condition, the patient feels difficulty
in breathing
The Symptoms of asthma vary
from person to person. The major
symptoms include shortness of breath (especially with exertion or at night), wheezing
(whistling sound when breathing out), cough and chest tightness.
The chemicals with ability to dilate the bronchi and bronchioles are used in the treatment
of asthma. Such medicine is given in the form of inhalers.

5. Lung Cancer:
Lung cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell divisions in the tissues of the lung. The
cells continue to divide without any control and form tumours. The cellular growth
may also invade adjacent tissues beyond the lungs.
The most common Symptoms are
shortness of breath, coughing (including coughing up blood) and weight loss.
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer-related deaths and is responsible for more
than 1.3 million deaths worldwide annually.
The Main Causes of any cancer include
carcinogens (such as those in cigarette
smoke), ionizing radiation and viral infection.
Smoking is the main cause of lung cancer.
This risk of lung cancer is significantly lower
in non smokers. Cigarette smoke contains over
50 known carcinogens.
Passive smoking (the inhalation of smoke
from another’s smoking) is also a cause of lung
cancer. The smoke from the burning end of a
cigarette is more dangerous than the smoke
from the filter end.
Eliminating tobacco smoking is a primary
goal in the prevention of lung cancer. The World Health Orgizanation has called for
governments to stop tobacco advertising to prevent young people from taking up
smoking.

Wonderful
ReplyDeleteNice post
ReplyDeleteVery nice
ReplyDeleteVery informative post
ReplyDeleteAwsome post
ReplyDeletewell done good work 👍
ReplyDelete